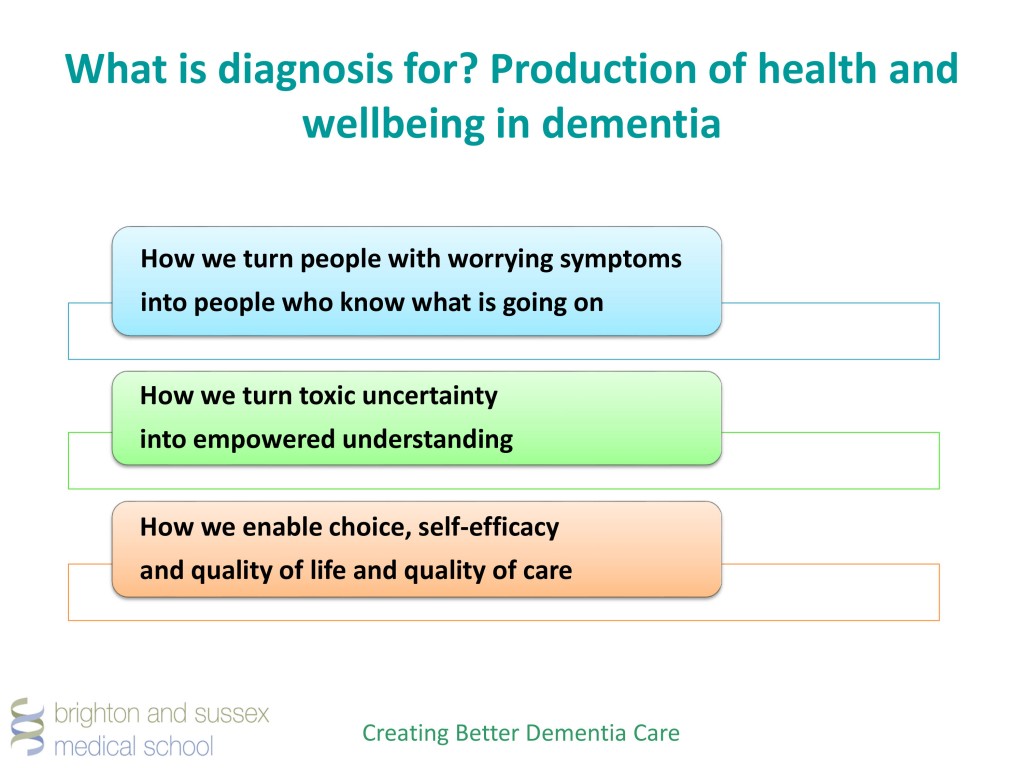
The penultimate chapter of my book will discuss palliative care and end of life care in dementia. This will be published in a book entitled ‘Enhancing health and wellbeing in dementia: care homes and care at home’ published by Jessica Kingsley in late 2015. I intend to discuss the following peer-reviewed papers. Please note that this list does not include websites or reports.
Chapter 12 Dying well in dementia
Aaltonen M, Raitanen J, Forma L, Pulkki J, Rissanen P, Jylhä M. Burdensome transitions at the end of life among long-term care residents with dementia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014 Sep;15(9):643-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2014.04.018. Epub 2014 Jun 7.
Agar M, Beattie E, Luckett T, Phillips J, Luscombe G, Goodall S, Mitchell G, Pond D, Davidson PM, Chenoweth L. Pragmatic cluster randomised controlled trial of facilitated family case conferencing compared with usual care for improving end of life care and outcomes in nursing home residents with advanced dementia and their families: the IDEAL study protocol. BMC Palliat Care. 2015 Nov 21;14(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12904-015-0061-8.
Ahearn DJ, Nidh N, Kallat A, Adenwala Y, Varman S. Offering older hospitalised patients the choice to die in their preferred place. Postgrad Med J. 2013 Jan;89(1047):20-4. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2012-131161. Epub 2012 Nov 9.
Albers G, Van den Block L, Vander Stichele R. The burden of caring for people with dementia at the end of life in nursing homes: a postdeath study among nursing staff. Int J Older People Nurs. 2014 Jun;9(2):106-17. doi: 10.1111/opn.12050. Epub 2014 May 10.
Andrews S, McInerney F, Toye C, Parkinson CA, Robinson A. Knowledge of Dementia: Do family members understand dementia as a terminal condition? Dementia (London). 2015 Sep 21. pii: 1471301215605630. [Epub ahead of print]
Arcand M. End-of-life issues in advanced dementia: Part 1: goals of care, decision-making process, and family education. Can Fam Physician. 2015 Apr;61(4):330-4.
Arcand M. End-of-life issues in advanced dementia: Part 2: management of poor nutritional intake, dehydration, and pneumonia. Can Fam Physician. 2015 Apr;61(4):337-41.
Ashton SE, Roe B, Jack B, McClelland B. End of life care: The experiences of advance care planning amongst family caregivers of people with advanced dementia – A qualitative study. Dementia (London). 2014 Sep 3. pii: 1471301214548521. [Epub ahead of print]
Barclay S, Froggatt K, Crang C, Mathie E, Handley M, Iliffe S, Manthorpe J, Gage H, Goodman C. Living in uncertain times: trajectories to death in residential care homes. Br J Gen Pract. 2014 Sep;64(626):e576-83. doi: 10.3399/bjgp14X681397.
Bayer A. Death with dementia–the need for better care. Age Ageing. 2006 Mar;35(2):101-2. Epub 2006 Jan 13.
Bernacki R, Hutchings M, Vick J, Smith G, Paladino J, Lipsitz S, Gawande AA, Block SD. Development of the Serious Illness Care Program: a randomised controlled trial of a palliative care communication intervention. BMJ Open. 2015 Oct 6;5(10):e009032. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009032.
Blandin K, Pepin R. Dementia grief: A theoretical model of a unique grief experience. Dementia (London). 2015 Apr 15. pii: 1471301215581081. [Epub ahead of print]
Boerner K, Burack OR, Jopp DS, Mock SE. Grief after patient death: direct care staff in nursing homes and homecare. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2015 Feb;49(2):214-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2014.05.023. Epub 2014 Jul 1.
Boogaard JA, van Soest-Poortvliet MC, Anema JR, Achterberg WP, Hertogh CM, de Vet HC, van der Steen JT. Feedback on end-of-life care in dementia: the study protocol of the FOLlow-up project. BMC Palliat Care. 2013 Aug 7;12(1):29. doi: 10.1186/1472-684X-12-29.
Borgstrom E, Walter T. Choice and compassion at the end of life: A critical analysis of recent English policy discourse. Soc Sci Med. 2015 Jul;136-137:99-105. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2015.05.013. Epub 2015 May 12.
Borgstrom E, Walter T. Choice and compassion at the end of life: A critical analysis of recent English policy discourse. Soc Sci Med. 2015 Jul;136-137:99-105. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2015.05.013. Epub 2015 May 12.
Brazil K, Carter G, Galway K, Watson M, van der Steen JT. General practitioners perceptions on advance care planning for patients living with dementia. BMC Palliat Care. 2015 Apr 23;14:14. doi: 10.1186/s12904-015-0019-x.
Brown MA, Sampson EL, Jones L, Barron AM. Prognostic indicators of 6-month mortality in elderly people with advanced dementia: a systematic review. Palliat Med. 2013 May;27(5):389-400. doi: 10.1177/0269216312465649. Epub 2012 Nov 22.
Brown R, Howard R, Candy B, Sampson EL. Opioids for agitation in dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 May 14;5:CD009705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009705.pub2.
Calanzani N, Moens K, Cohen J, Higginson IJ, Harding R, Deliens L, Toscani F, Ferreira PL, Bausewein C, Daveson BA, Gysels M, Ceulemans L, Gomes B; Project PRISMA. Choosing care homes as the least preferred place to die: a cross-national survey of public preferences in seven European countries. BMC Palliat Care. 2014 Oct 23;13:48. doi: 10.1186/1472-684X-13-48.
Calanzani N, Moens K, Cohen J, Higginson IJ, Harding R, Deliens L, Toscani F, Ferreira PL, Bausewein C, Daveson BA, Gysels M, Ceulemans L, Gomes B; Project PRISMA. Choosing care homes as the least preferred place to die: a cross-national survey of public preferences in seven European countries. BMC Palliat Care. 2014 Oct 23;13:48. doi: 10.1186/1472-684X-13-48.
Candy B, Elliott M, Moore K, Vickerstaff V, Sampson EL, Jones L. UK quality statements on end of life care in dementia: a systematic review of research evidence. BMC Palliat Care. 2015 Oct 19;14:51. doi: 10.1186/s12904-015-0047-6.
Candy B, Elliott M, Moore K, Vickerstaff V, Sampson EL, Jones L. UK quality statements on end of life care in dementia: a systematic review of research evidence. BMC Palliat Care. 2015 Oct 19;14:51. doi: 10.1186/s12904-015-0047-6.
Carter G, van der Steen JT, Galway K, Brazil K. General practitioners’ perceptions of the barriers and solutions to good-quality palliative care in dementia. Dementia (London). 2015 Apr 16. pii: 1471301215581227. [Epub ahead of print]
Casarett D, Kutner JS, Abrahm J; End-of-Life Care Consensus Panel. Life after death: a practical approach to grief and bereavement. Ann Intern Med. 2001 Feb 6;134(3):208-15.
Chochinov HM, Hack T, McClement S, Kristjanson L, Harlos M. Dignity in the terminally ill: a developing empirical model. Soc Sci Med. 2002 Feb;54(3):433-43.
Clark D, Armstrong M, Allan A, Graham F, Carnon A, Isles C. Imminence of death among hospital inpatients: Prevalent cohort study. Palliat Med. 2014 Mar 17;28(6):474-479. [Epub ahead of print]
Cohen LW, van der Steen JT, Reed D, Hodgkinson JC, van Soest-Poortvliet MC, Sloane PD, Zimmerman S. Family perceptions of end-of-life care for long-term care residents with dementia: differences between the United States and the Netherlands. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012 Feb;60(2):316-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03816.x. Epub 2012 Jan 30.
Coleman AM. End-of-life issues in caring for patients with dementia: the case for palliative care in management of terminal dementia. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2012 Feb;29(1):9-12. doi: 10.1177/1049909111410306. Epub 2011 Jun 10.
Connolly A, Sampson EL, Purandare N. End-of-life care for people with dementia from ethnic minority groups: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012 Feb;60(2):351-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03754.x.
Davies N, Maio L, van Riet Paap J, Mariani E, Jaspers B, Sommerbakk R, Grammatico D, Manthorpe J, Ahmedzai S, Vernooij-Dassen M, Iliffe S; IMPACT research team. Quality palliative care for cancer and dementia in five European countries: some common challenges. Aging Ment Health. 2014 May;18(4):400-10. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2013.843157. Epub 2013 Oct 17.
Davies N, Manthorpe J, Sampson EL, Iliffe S. After the Liverpool Care Pathway–development of heuristics to guide end of life care for people with dementia: protocol of the ALCP study. BMJ Open. 2015 Sep 2;5(9):e008832. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008832.
De Roo ML, Albers G, Deliens L, de Vet HC, Francke AL, Van Den Noortgate N, Van den Block L; EURO IMPACT. Physical and Psychological Distress Are Related to Dying Peacefully in Residents With Dementia in Long-Term Care Facilities. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2015 Jul;50(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2015.02.024. Epub 2015 Apr 4.
De Roo ML, van der Steen JT, Galindo Garre F, Van Den Noortgate N, Onwuteaka-Philipsen BD, Deliens L, Francke AL; EURO IMPACT. When do people with dementia die peacefully? An analysis of data collected prospectively in long-term care settings. Palliat Med. 2014 Mar;28(3):210-9. doi: 10.1177/0269216313509128. Epub 2013 Nov 29.
Dening KH, Greenish W, Jones L, Mandal U, Sampson EL. Barriers to providing end-of-life care for people with dementia: a whole-system qualitative study. BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2012 Jun;2(2):103-7. doi: 10.1136/bmjspcare-2011-000178. Epub 2012 Mar 1.
Dening KH, Jones L, Sampson EL. Preferences for end-of-life care: a nominal group study of people with dementia and their family carers. Palliat Med. 2013 May;27(5):409-17. doi: 10.1177/0269216312464094. Epub 2012 Nov 5.
Dening T, Dening KH. Palliative care in dementia: Does it work? Maturitas. 2016 Jan;83:1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2015.10.006. Epub 2015 Oct 22.
Dixon J, Matosevic T, Knapp M. The economic evidence for advance care planning: Systematic review of evidence. Palliat Med. 2015 Dec;29(10):869-84. doi: 10.1177/0269216315586659. Epub 2015 Jun 9.
Dougherty M, Harris PS, Teno J, Corcoran AM, Douglas C, Nelson J, Way D, Harrold JE, Casarett DJ. Hospice Care in Assisted Living Facilities Versus at Home: Results of a Multisite Cohort Study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015 Jun;63(6):1153-7. doi: 10.1111/jgs.13429.
Einterz SF, Gilliam R, Lin FC, McBride JM, Hanson LC. Development and testing of a decision aid on goals of care for advanced dementia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014 Apr;15(4):251-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2013.11.020. Epub 2014 Feb 6.
Elliott M, Harrington J, Moore K, Davis S, Kupeli N, Vickerstaff V, Gola A, Candy B, Sampson EL, Jones L. A protocol for an exploratory phase I mixed-methods study of enhanced integrated care for care home residents with advanced dementia: the Compassion Intervention. BMJ Open. 2014 Jun 17;4(6):e005661. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-005661.
Ersek M, Thorpe J, Kim H, Thomasson A, Smith D. Exploring End-of-Life Care in Veterans Affairs Community Living Centers. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015 Apr;63(4):644-50. doi: 10.1111/jgs.13348. Epub 2015 Mar 25.
Estabrooks CA, Hoben M, Poss JW, Chamberlain SA, Thompson GN, Silvius JL, Norton PG. Dying in a nursing home: treatable symptom burden and its link to modifiable features of work context. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2015 Jun 1;16(6):515-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2015.02.007. Epub 2015 Mar 21.
Ferreira PL, Bausewein C, Daveson BA, Gysels M, Ceulemans L, Gomes B; Project PRISMA. Choosing care homes as the least preferred place to die: a cross-national survey of public preferences in seven European countries. BMC Palliat Care. 2014 Oct 23;13:48. doi: 10.1186/1472-684X-13-48.
Finucane AM, Stevenson B, Moyes R, Oxenham D, Murray SA. Improving end-of-life care in nursing homes: implementation and evaluation of an intervention to sustain quality of care. Palliat Med. 2013 Sep;27(8):772-8. doi: 10.1177/0269216313480549. Epub 2013 Apr 23.
Fleming R, Kelly F, Stillfried G. ‘I want to feel at home': establishing what aspects of environmental design are important to people with dementia nearing the end of life. BMC Palliat Care. 2015 May 12;14:26. doi: 10.1186/s12904-015-0026-y.
Formiga F, Olmedo C, López Soto A, Pujol R. Dying in hospital of severe dementia: palliative decision-making analysis. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2004 Oct;16(5):420-1.
Frank JB. Evidence for grief as the major barrier faced by Alzheimer caregivers: a qualitative analysis. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2007 Dec-2008 Jan;22(6):516-27. doi: 10.1177/1533317507307787.
Froggatt K, Payne S. A survey of end-of-life care in care homes: issues of definition and practice. Health Soc Care Community. 2006 Jul;14(4):341-8.
Frohnhofen H, Hagen O, Heuer HC, Falkenhahn C, Willschrei P, Nehen HG. The terminal phase of life as a team-based clinical global judgment: prevalence and associations in an acute geriatric unit. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2011 Oct;44(5):329-35. doi: 10.1007/s00391-011-0180-7.
Garand L, Lingler JH, Deardorf KE, DeKosky ST, Schulz R, Reynolds CF 3rd, Dew MA. Anticipatory grief in new family caregivers of persons with mild cognitive impairment and dementia. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2012 Apr-Jun;26(2):159-65. doi: 10.1097/WAD.0b013e31822f9051.
Gjerberg E, Lillemoen L, Førde R, Pedersen R. End-of-life care communications and shared decision-making in Norwegian nursing homes–experiences and perspectives of patients and relatives. BMC Geriatr. 2015 Aug 19;15:103. doi: 10.1186/s12877-015-0096-y.
Gomes B, Calanzani N, Higginson IJ. Reversal of the British trends in place of death: time series analysis 2004-2010. Palliat Med. 2012 Mar;26(2):102-7. doi: 10.1177/0269216311432329. Epub 2012 Jan 18.
Gomes B, Calanzani N, Koffman J, Higginson IJ. Is dying in hospital better than home in incurable cancer and what factors influence this? A population-based study. BMC Med. 2015 Oct 9;13:235. doi: 10.1186/s12916-015-0466-5.
Goodman C, Amador S, Elmore N, Machen I, Mathie E. Preferences and priorities for ongoing and end-of-life care: a qualitative study of older people with dementia resident in care homes. Int J Nurs Stud. 2013 Dec;50(12):1639-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2013.06.008. Epub 2013 Jul 16.
Goodman C, Amador S, Elmore N, Machen I, Mathie E. Preferences and priorities for ongoing and end-of-life care: a qualitative study of older people with dementia resident in care homes. Int J Nurs Stud. 2013 Dec;50(12):1639-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2013.06.008. Epub 2013 Jul 16.
Goodman C, Amador S, Elmore N, Machen I, Mathie E. Preferences and priorities for ongoing and end-of-life care: a qualitative study of older people with dementia resident in care homes. Int J Nurs Stud. 2013 Dec;50(12):1639-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2013.06.008. Epub 2013 Jul 16.
Goodman C, Evans C, Wilcock J, Froggatt K, Drennan V, Sampson E, Blanchard M, Bissett M, Iliffe S. End of life care for community dwelling older people with dementia: an integrated review. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2010 Apr;25(4):329-37. doi: 10.1002/gps.2343.
Goodman C, Froggatt K, Amador S, Mathie E, Mayrhofer A. End of life care interventions for people with dementia in care homes: addressing uncertainty within a framework for service delivery and evaluation. BMC Palliat Care. 2015 Sep 17;14:42. doi: 10.1186/s12904-015-0040-0.
Gove D, Sparr S, Dos Santos Bernardo AM, Cosgrave MP, Jansen S, Martensson B, Pointon B, Tudose C, Holmerova I. Recommendations on end-of-life care for people with dementia. J Nutr Health Aging. 2010 Feb;14(2):136-9.
Grossman D, Rootenberg M, Perri GA, Yogaparan T, DeLeon M, Calabrese S, Grief CJ, Moore J, Gill A, Stilos K, Daines P, Zimmermann C, Mazzotta P. Enhancing communication in end-of-life care: a clinical tool translating between the Clinical Frailty Scale and the Palliative Performance Scale. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014 Aug;62(8):1562-7. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12926. Epub 2014 Jun 24.
Grubb C, Arthur A. Student nurses’ experience of and attitudes towards care of the dying: A cross-sectional study. Palliat Med. 2016 Jan;30(1):83-8. doi: 10.1177/0269216315616762. Epub 2015 Nov 17.
Hadjistavropoulos T, Herr K, Prkachin KM, Craig KD, Gibson SJ, Lukas A, Smith JH. Pain assessment in elderly adults with dementia. Lancet Neurol. 2014 Dec;13(12):1216-27. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70103-6. Epub 2014 Nov 10.
Hall S, Kolliakou A, Petkova H, Froggatt K, Higginson IJ. Interventions for improving palliative care for older people living in nursing care homes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Mar 16;(3):CD007132. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007132.pub2.
Handley M, Goodman C, Froggatt K, Mathie E, Gage H, Manthorpe J, Barclay S, Crang C, Iliffe S. Living and dying: responsibility for end-of-life care in care homes without on-site nursing provision – a prospective study. Health Soc Care Community. 2014 Jan;22(1):22-9. doi: 10.1111/hsc.12055. Epub 2013 May 29.
Harris P, Wong E, Farrington S, Craig TR, Harrold JK, Oldanie B, Teno JM, Casarett DJ. Patterns of functional decline in hospice: what can individuals and their families expect? J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013 Mar;61(3):413-7. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12144. Epub 2013 Jan 24.
Hendriks SA, Smalbrugge M, Hertogh CM, van der Steen JT. Dying with dementia: symptoms, treatment, and quality of life in the last week of life. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2014 Apr;47(4):710-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2013.05.015. Epub 2013 Jul 31.
Hennings J, Froggatt K, Payne S. Spouse caregivers of people with advanced dementia in nursing homes: a longitudinal narrative study. Palliat Med. 2013 Jul;27(7):683-91. doi: 10.1177/0269216313479685. Epub 2013 Mar 13.
Hockley J, Watson J, Oxenham D, Murray SA. The integrated implementation of two end-of-life care tools in nursing care homes in the UK: an in-depth evaluation. Palliat Med. 2010 Dec;24(8):828-38. doi: 10.1177/0269216310373162. Epub 2010 Jul 27.
Holley CK, Mast BT. The impact of anticipatory grief on caregiver burden in dementia caregivers. Gerontologist. 2009 Jun;49(3):388-96. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnp061. Epub 2009 Apr 22.
Houttekier D, Cohen J, Bilsen J, Addington-Hall J, Onwuteaka-Philipsen BD, Deliens L. Place of death of older persons with dementia. A study in five European countries. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010 Apr;58(4):751-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.02771.x.
Houttekier D, Vandervoort A, Van den Block L, van der Steen JT, Vander Stichele R, Deliens L. Hospitalizations of nursing home residents with dementia in the last month of life: results from a nationwide survey. Palliat Med. 2014 Oct;28(9):1110-7. doi: 10.1177/0269216314535962. Epub 2014 May 27.
Hughes JC, Robinson L, Volicer L. Specialist palliative care in dementia. BMJ. 2005 Jan 8;330(7482):57-8.
Ikegami N, Ikezaki S. Nursing homes and end-of-life care in Japan. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2013 Oct;14(10):718-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2013.02.008. Epub 2013 Apr 3.
Jansen K, Schaufel MA, Ruths S. Drug treatment at the end of life: an epidemiologic study in nursing homes. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2014 Dec;32(4):187-92. doi: 10.3109/02813432.2014.972068. Epub 2014 Nov 3.
Johansson ÅK, Grimby A. Grief among demented elderly individuals: a pilot study. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2013 Aug;30(5):445-9. doi: 10.1177/1049909112457009. Epub 2012 Aug 16.
Johansson AK, Sundh V, Wijk H, Grimby A. Anticipatory grief among close relatives of persons with dementia in comparison with close relatives of patients with cancer. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2013 Feb;30(1):29-34. doi: 10.1177/1049909112439744. Epub 2012 Apr 10.
Johnson KS, Elbert-Avila K, Kuchibhatla M, Tulsky JA. Characteristics and outcomes of hospice enrollees with dementia discharged alive. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012 Sep;60(9):1638-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2012.04117.x. Epub 2012 Aug 20.
Johnston B, Larkin P, Connolly M, Barry C, Narayanasamy M, Östlund U, McIlfatrick S. Dignity-conserving care in palliative care settings: An integrative review. J Clin Nurs. 2015 Jul;24(13-14):1743-72. doi: 10.1111/jocn.12791. Epub 2015 Feb 23.
Johnston B, Lawton S, Pringle J. ‘This is my story, how I remember it': In-depth analysis of Dignity Therapy documents from a study of Dignity Therapy for people with early stage dementia. Dementia (London). 2015 Sep 15. pii: 1471301215605629. [Epub ahead of print]
Johnston B, Pringle J, Gaffney M, Narayanasamy M, McGuire M, Buchanan D. The dignified approach to care: a pilot study using the patient dignity question as an intervention to enhance dignity and person-centred care for people with palliative care needs in the acute hospital setting. BMC Palliat Care. 2015 Apr 9;14:9. doi: 10.1186/s12904-015-0013-3. eCollection 2015.
Jones L, Candy B, Davis S, Elliott M, Gola A, Harrington J, Kupeli N, Lord K, Moore K, Scott S, Vickerstaff V, Omar RZ, King M, Leavey G, Nazareth I, Sampson EL. Development of a model for integrated care at the end of life in advanced dementia: A whole systems UK-wide approach. Palliat Med. 2015 Sep 9. pii: 0269216315605447. [Epub ahead of print]
Jones L, Harrington J, Scott S, Davis S, Lord K, Vickerstaff V, Round J, Candy B, Sampson EL. CoMPASs: IOn programme (Care Of Memory Problems in Advanced Stages of dementia: Improving Our Knowledge): protocol for a mixed methods study. BMJ Open. 2012 Nov 27;2(6). pii: e002265. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2012-002265. Print 2012.
Karacsony S, Chang E, Johnson A, Good A, Edenborough M. Measuring nursing assistants’ knowledge, skills and attitudes in a palliative approach: A literature review. Nurse Educ Today. 2015 Dec;35(12):1232-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2015.05.008. Epub 2015 May 21.
Kinley J, Froggatt K, Bennett MI. The effect of policy on end-of-life care practice within nursing care homes: a systematic review. Palliat Med. 2013 Mar;27(3):209-20. doi: 10.1177/0269216311432899. Epub 2012 Jan 4.
Klapwijk MS, Caljouw MA, van Soest-Poortvliet MC, van der Steen JT, Achterberg WP. Symptoms and treatment when death is expected in dementia patients in long-term care facilities. BMC Geriatr. 2014 Sep 2;14:99. doi: 10.1186/1471-2318-14-99.
Kmietowicz Z. Most common cause of death in England and Wales in 2013 was heart disease in men and dementia in women. BMJ. 2015 Mar 2;350:h1156. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h1156.
Knapp M, King D, Romeo R, Schehl B, Barber J, Griffin M, Rapaport P, Livingston D, Mummery C, Walker Z, Hoe J, Sampson EL, Cooper C, Livingston G. Cost effectiveness of a manual based coping strategy programme in promoting the mental health of family carers of people with dementia (the START (STrAtegies for RelaTives) study): a pragmatic randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2013 Oct 25;347:f6342. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f6342.
Koopmans RT, van der Sterren KJ, van der Steen JT. The ‘natural’ endpoint of dementia: death from cachexia or dehydration following palliative care? Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007 Apr;22(4):350-5.
Koppitz A, Bosshard G, Schuster DH, Hediger H, Imhof L. Type and course of symptoms demonstrated in the terminal and dying phases by people with dementia in nursing homes. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2015 Feb;48(2):176-83. doi: 10.1007/s00391-014-0668-z.
Kuhn DR, Forrest JM. Palliative care for advanced dementia: a pilot project in 2 nursing homes. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2012 Feb;27(1):33-40. doi: 10.1177/1533317511432732. Epub 2012 Jan 31.
Large S, Slinger R. Grief in caregivers of persons with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementia: a qualitative synthesis. Dementia (London). 2015 Mar;14(2):164-83. doi: 10.1177/1471301213494511. Epub 2013 Jul 11.
Lawrence V, Samsi K, Murray J, Harari D, Banerjee S. Dying well with dementia: qualitative examination of end-of-life care. Br J Psychiatry. 2011 Nov;199(5):417-22. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.111.093989. Epub 2011 Sep 22.
Lee J, Cheng J, Au KM, Yeung F, Leung MT, Ng J, Hui E, Lo R, Woo J. Improving the quality of end-of-life care in long-term care institutions. J Palliat Med. 2013 Oct;16(10):1268-74. doi: 10.1089/jpm.2013.0190. Epub 2013 Sep 5.
Lee RP, Bamford C, Exley C, Robinson L. Expert views on the factors enabling good end of life care for people with dementia: a qualitative study. BMC Palliat Care. 2015 Jul 25;14:32. doi: 10.1186/s12904-015-0028-9.
Li Q, Zheng NT, Temkin-Greener H. Quality of end-of-life care of long-term nursing home residents with and without dementia. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013 Jul;61(7):1066-73. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12330. Epub 2013 Jun 17.
Liew TM. Applicability of the pre-death grief concept to dementia family caregivers in Asia. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2015 Nov 10. doi: 10.1002/gps.4387. [Epub ahead of print]
Lippa CF. Focusing on the caregiver: grief in dementia caregiving. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2010 Feb;25(1):7-8.
Long CO, Sowell EJ, Hess RK, Alonzo TR. Development of the questionnaire on palliative care for advanced dementia (qPAD). Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2012 Nov;27(7):537-43. doi: 10.1177/1533317512459793. Epub 2012 Sep 20.
Mahin-Babaei F, Hilal J, Hughes JC. The basis, ethics and provision of palliative care for dementia: A review. Maturitas. 2016 Jan;83:3-8. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2015.09.003. Epub 2015 Sep 16.
Mathie E, Goodman C, Crang C, Froggatt K, Iliffe S, Manthorpe J, Barclay S. An uncertain future: the unchanging views of care home residents about living and dying. Palliat Med. 2012 Jul;26(5):734-43. doi: 10.1177/0269216311412233. Epub 2011 Jun 22.
McCarty CE, Volicer L. Hospice access for individuals with dementia. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2009 Dec-2010 Jan;24(6):476-85. doi: 10.1177/1533317509348207. Epub 2009 Oct 7.
McKellar D, Ng F, Chur-Hansen A. Is death our business? Philosophical conflicts over the end-of-life in old age psychiatry. Aging Ment Health. 2015 Apr 14:1-11. [Epub ahead of print]
Meichsner F, Schinköthe D, Wilz G. Managing Loss and Change: Grief Interventions for Dementia Caregivers in a CBT-Based Trial. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2015 Aug 26. pii: 1533317515602085. [Epub ahead of print]
Merel SE, DeMers S, Vig E. Palliative care in advanced dementia. Clin Geriatr Med. 2014 Aug;30(3):469-92. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2014.04.004. Epub 2014 Jun 12.
Meuser TM, Marwit SJ. A comprehensive, stage-sensitive model of grief in dementia caregiving. Gerontologist. 2001 Oct;41(5):658-70.
Mitchell G. Palliative and end-of-life decision-making in dementia care. Int J Palliat Nurs. 2015 Nov;21(11):536-41. doi: 10.12968/ijpn.2015.21.11.536.
Mitchell SL, Black BS, Ersek M, Hanson LC, Miller SC, Sachs GA, Teno JM, Morrison RS. Advanced dementia: state of the art and priorities for the next decade. Ann Intern Med. 2012 Jan 3;156(1 Pt 1):45-51. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-156-1-201201030-00008.
Mystakidou K, Parpa E, Tsilika E, Athanasouli P, Pathiaki M, Galanos A, Pagoropoulou A, Vlahos L. Preparatory grief, psychological distress and hopelessness in advanced cancer patients. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2008 Mar;17(2):145-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2354.2007.00825.x.
Nourhashémi F, Gillette S, Cantet C, Stilmunkes A, Saffon N, Rougé-Bugat ME, Vellas B, Rolland Y. End-of-life care for persons with advanced Alzheimer disease: design and baseline data from the ALFINE study. J Nutr Health Aging. 2012 May;16(5):457-61.
Noyes BB, Hill RD, Hicken BL, Luptak M, Rupper R, Dailey NK, Bair BD. The role of grief in dementia caregiving. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2010 Feb;25(1):9-17. doi: 10.1177/1533317509333902.
O’Halloran P. After the Liverpool Care Pathway clear guidance and support on end-of-life care is needed. Evid Based Nurs. 2016 Jan;19(1):27. doi: 10.1136/eb-2015-102170. Epub 2015 Sep 16.
Oliver DP, Washington K, Kruse RL, Albright DL, Lewis A, Demiris G. Hospice family members’ perceptions of and experiences with end-of-life care in the nursing home. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014 Oct;15(10):744-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2014.05.014. Epub 2014 Jul 10.
Oosterman JM, Hendriks H, Scott S, Lord K, White N, Sampson EL. When pain memories are lost: a pilot study of semantic knowledge of pain in dementia. Pain Med. 2014 May;15(5):751-7. doi: 10.1111/pme.12336. Epub 2014 Jan 8.
Östlund U, Brown H, Johnston B. Dignity conserving care at end-of-life: a narrative review. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2012 Sep;16(4):353-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2011.07.010. Epub 2011 Sep 13.
Passoni S, Toraldo A, Villa B, Bottini G. Prolonged grief in caregivers of community-dwelling dementia patients. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2015 Mar;30(2):192-200. doi: 10.1177/1533317514542643. Epub 2014 Jul 9.
Peacock SC, Hammond-Collins K, Forbes DA. The journey with dementia from the perspective of bereaved family caregivers: a qualitative descriptive study. BMC Nurs. 2014 Nov 27;13(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12912-014-0042-x. eCollection 2014.
Penders YW, Albers G, Deliens L, Vander Stichele R, Van den Block L; EURO IMPACT. Awareness of dementia by family carers of nursing home residents dying with dementia: a post-death study. Palliat Med. 2015 Jan;29(1):38-47. doi: 10.1177/0269216314542261. Epub 2014 Jul 18.
Powers BA, Watson NM. Meaning and practice of palliative care for nursing home residents with dementia at end of life. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2008 Aug-Sep;23(4):319-25. doi: 10.1177/1533317508316682. Epub 2008 May 4.
Pringle J, Johnston B, Buchanan D. Dignity and patient-centred care for people with palliative care needs in the acute hospital setting: A systematic review. Palliat Med. 2015 Sep;29(8):675-94. doi: 10.1177/0269216315575681. Epub 2015 Mar 23.
Raymond M, Warner A, Davies N, Baishnab E, Manthorpe J, Iliffe S; IMPACT research team. Evaluating educational initiatives to improve palliative care for people with dementia: a narrative review. Dementia (London). 2014 May;13(3):366-81. doi: 10.1177/1471301212474140. Epub 2013 Feb 7.
Raymond M, Warner A, Davies N, Iliffe S, Manthorpe J, Ahmedzhai S. Palliative care services for people with dementia: a synthesis of the literature reporting the views and experiences of professionals and family carers. Dementia (London). 2014 Jan;13(1):96-110. doi: 10.1177/1471301212450538. Epub 2012 Aug 10.
Reinhardt JP, Chichin E, Posner L, Kassabian S. Vital conversations with family in the nursing home: preparation for end-stage dementia care. J Soc Work End Life Palliat Care. 2014;10(2):112-26. doi: 10.1080/15524256.2014.906371.
Reyniers T, Houttekier D, Cohen J, Pasman HR, Deliens L. The acute hospital setting as a place of death and final care: a qualitative study on perspectives of family physicians, nurses and family carers. Health Place. 2014 May;27:77-83. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2014.02.002. Epub 2014 Feb 25.
Ribbe MW, Ljunggren G, Steel K, Topinková E, Hawes C, Ikegami N, Henrard JC, Jónnson PV. Nursing homes in 10 nations: a comparison between countries and settings. Age Ageing. 1997 Sep;26 Suppl 2:3-12.
Rogers IR, Lukin B. Applying palliative care principles and practice to emergency medicine. Emerg Med Australas. 2015 Nov 11. doi: 10.1111/1742-6723.12494. [Epub ahead of print]
Round J, Sampson EL, Jones L. A framework for understanding quality of life in individuals without capacity. Qual Life Res. 2014 Mar;23(2):477-84. doi: 10.1007/s11136-013-0500-z. Epub 2013 Aug 22.
Ryan T, Ingleton C. Most hospices and palliative care programmes in the USA serve people with dementia; lack of awareness, need for respite care and reimbursement policies are the main barriers to providing this care. Evid Based Nurs. 2011 Apr;14(2):40-1. doi: 10.1136/ebn.14.2.40.
Sachs GA, Shega JW, Cox-Hayley D. Barriers to excellent end-of-life care for patients with dementia. J Gen Intern Med. 2004 Oct;19(10):1057-63.
Sampson E, Mandal U, Holman A, Greenish W, Dening KH, Jones L. Improving end of life care for people with dementia: a rapid participatory appraisal. BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2012 Jun;2(2):108-14. doi: 10.1136/bmjspcare-2011-000177. Epub 2012 Mar 31.
Sampson EL, Blanchard MR, Jones L, Tookman A, King M. Dementia in the acute hospital: prospective cohort study of prevalence and mortality. Br J Psychiatry. 2009 Jul;195(1):61-6. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.108.055335.
Sampson EL, Burns A, Richards M. Improving end-of-life care for people with dementia. Br J Psychiatry. 2011 Nov;199(5):357-9. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.111.097030.
Sampson EL, Jones L, Thuné-Boyle IC, Kukkastenvehmas R, King M, Leurent B, Tookman A, Blanchard MR. Palliative assessment and advance care planning in severe dementia: an exploratory randomized controlled trial of a complex intervention. Palliat Med. 2011 Apr;25(3):197-209. doi: 10.1177/0269216310391691. Epub 2011 Jan 12.
Sampson EL, Leurent B, Blanchard MR, Jones L, King M. Survival of people with dementia after unplanned acute hospital admission: a prospective cohort study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013 Oct;28(10):1015-22. doi: 10.1002/gps.3919. Epub 2012 Dec 21.
Sampson EL, Thuné-Boyle I, Kukkastenvehmas R, Jones L, Tookman A, King M, Blanchard MR. Palliative care in advanced dementia; A mixed methods approach for the development of a complex intervention. BMC Palliat Care. 2008 Jul 11;7:8. doi: 10.1186/1472-684X-7-8.
Sampson EL, van der Steen JT, Pautex S, Svartzman P, Sacchi V, Van den Block L, Van Den Noortgate N. European palliative care guidelines: how well do they meet the needs of people with impaired cognition? BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2015 Sep;5(3):301-5. doi: 10.1136/bmjspcare-2014-000813. Epub 2015 Apr 13.
Sampson EL, White N, Leurent B, Scott S, Lord K, Round J, Jones L. Behavioural and psychiatric symptoms in people with dementia admitted to the acute hospital: prospective cohort study. Br J Psychiatry. 2014 Sep;205(3):189-96. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.113.130948. Epub 2014 Jul 24.
Sampson EL, White N, Lord K, Leurent B, Vickerstaff V, Scott S, Jones L. Pain, agitation, and behavioural problems in people with dementia admitted to general hospital wards: a longitudinal cohort study. Pain. 2015 Apr;156(4):675-83. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000095.
Sampson EL. Palliative care for people with dementia. Br Med Bull. 2010;96:159-74. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldq024. Epub 2010 Jul 30.
Seymour JE, Kumar A, Froggatt K. Do nursing homes for older people have the support they need to provide end-of-life care? A mixed methods enquiry in England. Palliat Med. 2011 Mar;25(2):125-38. doi: 10.1177/0269216310387964. Epub 2011 Jan 31.
Shuter P, Beattie E, Edwards H. An Exploratory Study of Grief and Health-Related Quality of Life for Caregivers of People With Dementia. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2013 Dec 31;29(4):379-385. [Epub ahead of print]
Sleeman KE, Davies JM, Verne J, Gao W, Higginson IJ. The changing demographics of inpatient hospice death: Population-based cross-sectional study in England, 1993-2012. Palliat Med. 2016 Jan;30(1):45-53. doi: 10.1177/0269216315585064. Epub 2015 May 19.
Sleeman KE, Ho YK, Verne J, Gao W, Higginson IJ; GUIDE_Care project. Reversal of English trend towards hospital death in dementia: a population-based study of place of death and associated individual and regional factors, 2001-2010. BMC Neurol. 2014 Mar 26;14:59. doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-14-59.
Torke AM, Holtz LR, Hui S, Castelluccio P, Connor S, Eaton MA, Sachs GA. Palliative care for patients with dementia: a national survey. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010 Nov;58(11):2114-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.03141.x.
Toscani F, van der Steen JT, Finetti S, Giunco F, Pettenati F, Villani D, Monti M, Gentile S, Charrier L, Di Giulio P; End of Life Observatory-Prospective Study on DEmentia Patients Care (EoLO-PSODEC) Research Group; End of Life Observatory-Prospective Study on DEmentia Patients Care EoLO-PSODEC Research Group. Critical decisions for older people with advanced dementia: a prospective study in long-term institutions and district home care. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2015 Jun 1;16(6):535.e13-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2015.02.012. Epub 2015 Apr 2.
Toye C, Robinson AL, Jiwa M, Andrews S, McInerney F, Horner B, Holloway K, Stratton B. Developing and testing a strategy to enhance a palliative approach and care continuity for people who have dementia: study overview and protocol. BMC Palliat Care. 2012 Apr 2;11:4. doi: 10.1186/1472-684X-11-4.
Unroe KT, Sachs GA, Dennis ME, Hickman SE, Stump TE, Tu W, Callahan CM. Hospice use among nursing home and non-nursing home patients. J Gen Intern Med. 2015 Feb;30(2):193-8. doi: 10.1007/s11606-014-3080-x. Epub 2014 Nov 6.
van der Steen JT, Radbruch L, Hertogh CM, de Boer ME, Hughes JC, Larkin P, Francke AL, Jünger S, Gove D, Firth P, Koopmans RT, Volicer L; European Association for Palliative Care (EAPC). White paper defining optimal palliative care in older people with dementia: a Delphi study and recommendations from the European Association for Palliative Care. Palliat Med. 2014 Mar;28(3):197-209. doi: 10.1177/0269216313493685. Epub 2013 Jul 4.
van Riet Paap J, Mariani E, Chattat R, Koopmans R, Kerhervé H, Leppert W, Forycka M, Radbruch L, Jaspers B, Vissers K, Vernooij-Dassen M, Engels Y; IMPACT research team. Identification of the palliative phase in people with dementia: a variety of opinions between healthcare professionals. BMC Palliat Care. 2015 Nov 4;14:56. doi: 10.1186/s12904-015-0053-8.
van Riet Paap J, Vernooij-Dassen M, Dröes RM, Radbruch L, Vissers K, Engels Y; IMPACT research team. Consensus on quality indicators to assess the organisation of palliative cancer and dementia care applicable across national healthcare systems and selected by international experts. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014 Sep 17;14:396. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-14-396.
van Soest-Poortvliet MC, van der Steen JT, de Vet HC, Hertogh CM, Deliens L, Onwuteaka-Philipsen BD. Comfort goal of care and end-of-life outcomes in dementia: A prospective study. Palliat Med. 2015 Jun;29(6):538-46. doi: 10.1177/0269216315570409. Epub 2015 Feb 17.
Vlachogianni A, Efthymiou A, Potamianou D, Sakka P, Orgeta V. Life after care: psychological adjustment to bereavement in family carers of people with dementia. Int Psychogeriatr. 2015 Dec 9:1-9. [Epub ahead of print]
Watkin L, Blanchard MR, Tookman A, Sampson EL. Prospective cohort study of adverse events in older people admitted to the acute general hospital: risk factors and the impact of dementia. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;27(1):76-82. doi: 10.1002/gps.2693. Epub 2011 Feb 28.
Zahradnik EK, Grossman H. Palliative care as a primary therapeutic approach in advanced dementia: a narrative review. Clin Ther. 2014 Nov 1;36(11):1512-7. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.10.006. Epub 2014 Oct 29.
Zimmerman S, Cohen L, van der Steen JT, Reed D, van Soest-Poortvliet MC, Hanson LC, Sloane PD. Measuring end-of-life care and outcomes in residential care/assisted living and nursing homes. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2015 Apr;49(4):666-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2014.08.009. Epub 2014 Sep 6.