I’ll be blunt. It’s my dream for the #NHS to run a proactive not reactive service, promoting the whole person living well with dementia.
The Australian jurisdiction have recently provided some helpful inroads here.
The narrative has changed from one of incessantly referring to people living with dementia as a ‘burden’ on the rest of society. For example, to push a sense of urgency that we have an ‘ageing population timebomb’, the cost of the ageing people with dementia flies completely in the face of other public health campaigns which emphasise, for example, “dementia is not a natural part of ageing”.
“The NHS as a whole and individual hospitals recognise that dementia is a significant, growing and costly problem for them” is the opening gambit of the Alzheimer’s Society “Counting the cost” report.
An easy to use online resource, Valuing People from Alzheimer’s Australia has been developed in collaboration with community aged care providers who have helpful in stablishing a person centred approach to service delivery.
Person centred care is a development to provide ervices provided in a way that is respectful of, and responsive to, the preferences, needs and values of people and those in the care and support network.
I cannot recommend this resource highly enough. The main source is here.
In fact, it summarises succinctly the conclusions I came to after my exploration of personhood in my book ‘Living well with dementia’. The late great Prof Tom Kitwood said of personhood, “It is a standing or status that is bestowed upon one human being, by others, in the context of relationship and social being. It implies recognition, respect and trust”.
If a Labour government is elected on May 8th 2015, the first necessary step is to legislate for the repeal of the Health and Social Care Act (2012) and to enact new legislation to allow for integrated packages provided they are justified by clinical outcome. For this to happen, it will be necessary for Labour to undergo a ‘conscious uncoupling’ from all the baggage of EU competition law. For this, it is essential also that the UK government is able to carve out provisions from the investor protection clauses and/or the rest of the EU-US free trade treaty (TTIP).
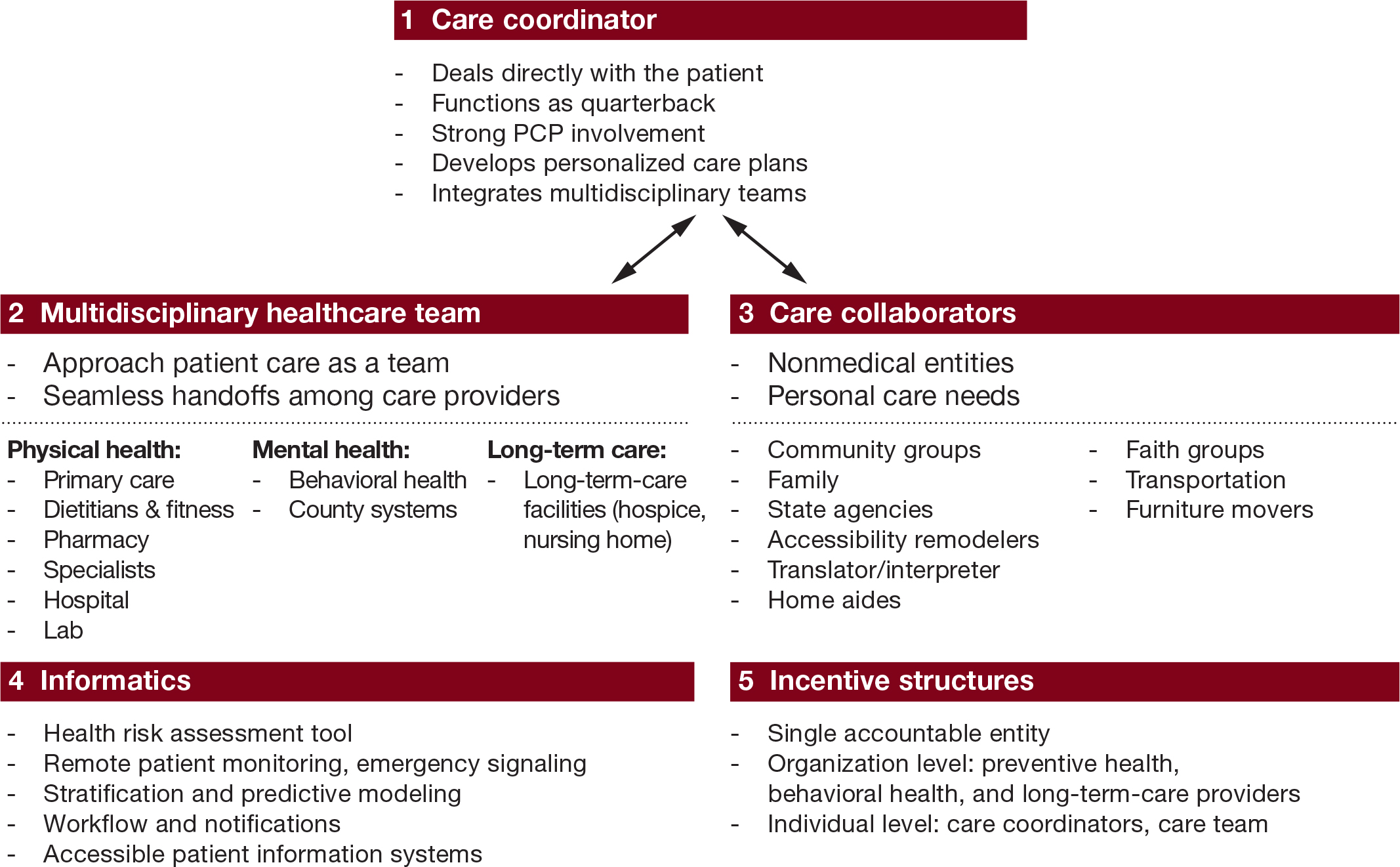
The “whole person care model” has become attractive to those who wish to break down silos between different physical health, mental health and social care “silos”. It has been worked up in various guises by various parties.
A helpful construct is provided in the document, “Healthcare for complex populations: the power of whole-person care models” originally published by Booz & Company in 2013.
A major problem with dementia care, however it is delivered, is that it is full of divisions: public vs private care, fragmented vs national care, competitive vs integrated models. Operating in silos can’t work because of the nature of the dementias: the mood and cognition of a person with dementia profoundly affects how they might interact with the outside world, for example perform activities in the outside world. And we know that taking part in leisure activities can promote a good quality of life.
Their model is, though, a useful starting point.
Dementia cannot be only addressed by the medical model. In fact, it is my sincere belief that it would be highly dangerous to put all your eggs in the physical health basket, without due attention to mental health or social care. For example, last week in Stockholm, the international conference on Parkinson’s disease, a condition typified by a resting tremor, rigidity and slowness of movement, which can progress to a dementia, often is found to have as heralding symptoms changes in cognition and mood.
So it’s pretty clear to me that we will have to embark on a system of multidisciplinary professionals who could all have a part to play in the wellbeing of a person with dementia, depending on his or her own stage in life, and ability or need to live independently. “Care coordinators” have traditionally been defined incredibly badly, but we do need such an identity to navigate people with dementia, and actors in the care and support network, through the maze.
“Care collaborators” in their construct are very wonkily articulated, like “pre-distribution”, but the concept is not stupid. In fact it is very good. One idea is that people with dementia could act as support as other people with dementia, for people on receiving a diagnosis of dementia. The rationale for this is that people living with long term conditions, such as for example recovery from alcoholism, often draw much support from other people living with other long term conditions, away from a medical model. There needs to be safeguards in the system to safeguard against a lot of unpaid goodwill (which currently exists in the system.)
Informatics would have a really helpful rôle here, being worked up in telecare and assistive technology. But even simple disruptions such as a person living with dementia at risk of falling from problems with spatial depth perception being able to ‘hot email’ a care coordinator about perceived problems could trigger, say, an early warning system. And with various agents in the provision of care being involved in differing extents it will be up to NHS England to work out how best to implement a single accountable tariff. Falls are just the sort of ‘outcome metric’ which could be used to determine whether this policy of ‘whole person care’ for people living with dementia is working. And, even though everyone ‘trots it out’, the performance on avoided hospital admissions could be put into the mixer. It’s already well recognised that people with dementia can become very disoriented in hospital, and, and despite the best efforts of those trying to improve the acute care pathway, people with dementia can often be better off away from hospital in the community. But it’s imperative that care in the community is not a second-rate service compared to secondary care, and proper resourcing of community whole person care is essential for this before any reconfiguration in acute hospital services.
But the private sector has become such a ‘bogey term’ after arguably the current Government overplayed their hand with the £3bn Act of parliament which turbo-boosted a transfer of resource allocation from the public to private sector. Any incoming government will have to be particularly sensitive to this, as this is a risk in strategy for the NHS.
In October 2005, Harold Sirkin, Perry Keenan and Alan Jackson published a highly influential article in the Harvard Business Review entitled “The hard side of change management“. Whilst much play has in fact been made of politicians having to be distant from running the NHS, a completely lubricous line of attack when it is alleged that Jeremy Hunt talks regularly to senior managers and regulators in the NHS, the benefits of clear political leadership from an incoming Labour government are clear.
Andy Burnham MP has already nailed his colours to the mast of ‘whole person care’ on various occasions, and it is clear that the success of this ambitious large scale transformation depends on clear leadership and teamwork from bright managers. Take for example the DICE criteria from Sirkin, Keenan and Jackson:
But this is perfectly possible from an incoming Government. The National Health Service has a chance to lead on something truly innovative, learning from the experience of other jurisdictions such as Australia and the USA.
As alluded to in the new resource from the Alzheimer’s Australia, this cultural change will require substantial ‘unfreezing’ from the current mindset for provision of care for people with dementia. It will require a change in explicit and implicit sources of knowledge and behaviours, and will need to be carefully brought about by learning from the successes and failures of pockets of implementation.
The whole project’s pretty high risk, but the rewards for people living with dementia, and members of the care and support network, are potentially vast. But it does require the implementation of a very clear vision.
[First posted on the ‘Living well with dementia‘ blog]